How Domain Registration Works (step by step)
If you recently bought a domain name then one of your questions might be how domain registration really works.
Here is a real example of a .com domain name registration:
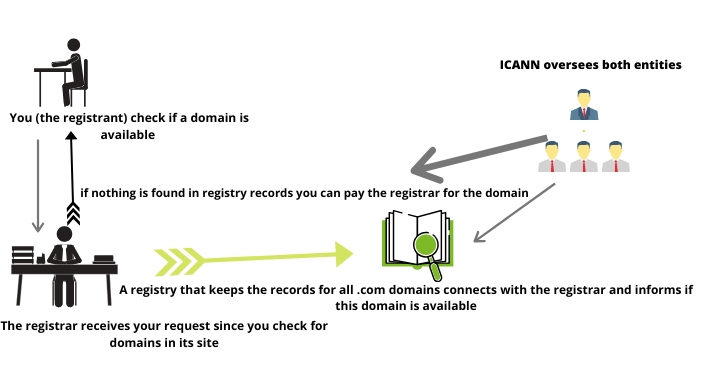
We will explain each step in every detail:
1.)Registrant Tries to Buy a Domain Name
When you visit a site that sells domains then you have an option to type a combination of keywords, select the extension (ex.com) you want and then check if the domain is available. If it is available then you can add it to the cart and buy it. During this process, a fast check happened in the background. We will discuss that part in the second step.
There is also another way to check if a domain name is available. By using this tool whois.net or any similar whois database you can find out for the availability of a domain name. Additionally, you can see more details such as when this domain was registered and when it will expire.
There are cases that even if the domain is not available you can still buy it. Some registrars (the retailers) allow other domain name owners to put them for sale. There are no limitations to the price tags.
This the reason why you see some prices far away from the normal. Sometimes registrars have cooperations with secondary marketplaces that their sole purpose is to sell this type of domain.
The person that owns a domain name is called the registrant. Anyone can be a registrant if he is in legal age (16 or 18 based on different policies) for the .com domain. In contrast, some country domains like .de (Germany) have as a requirement a valid country address. For some other domain extension, you need to represent a certain type of entity (like. gov for government agencies).
2.)Registrar Connects to Registry
As we discussed in step 1 when you type a domain name on Registrar’s search bar a quick check happens on background. A registry has all the records related to the domain names of certain extensions (in our example for .com). If some .com is already registered it would be in its records.
*Technically they connect by using the Extensible Provisioning Protocol which considers very safe for this type of communication.
3.)Registry Returns the Results
The registry informs the registrar if the domain name is available or not. If there is no such record the end-user (registrant) can move on with the completion of purchase. Otherwise, a message will pop-up and will mark the domain as unavailable.
4.)Domain Registration Happens
For domain registration, it is mandatory that you provide some contact details. These details are Full name, Email, phone, and address. After the registration, you can make changes whenever you want and those updates will be transferred to the registry too. You can even change registrar and the process can take from some minutes up to 7 days.
I would like also to mention that you don’t “typically” own the domain but you lease it for a certain time. In reality, you can keep the domain for decades you just need to renew it after some years. You can prepay for 1 up to 10 years or set the domain to auto-renew (provide a card that you have always money loaded there!).
Registrar Brief Explanation And Examples
Registrars are companies that regulatory bodies (such as ICANN for .com) allow them to provide registration services to end-users. In that sense, they are the retailers in the industry. There are big fees associated with the role of a registrar.
They need to pay a $3,500 application fee and $4000 per year after they get approval from ICANN. They need to fulfill other requirements such as having enough working capital, employees and insurance for their business operations.
You can see here the accredited registrars from ICANN. Some of the big names in the industry are Godaddy and Namecheap. If you notice these companies can offer other services too and they are not limited to domain names. Additionally, they can offer web hosting, email, and other related services.
Registry Brief Explanation And Examples
A registry is considered as the wholesaler of the industry in most cases. Some registries are companies, some are government-related organizations and others are nonprofits. Registries have responsibilities for specific domain name extensions. For example, Verisign is responsible for .com, .net, .name, .cc, .tv, .edu, .gov and .jobs domains. Nominet is responsible for .uk domain and Denic is responsible for .de domains.
A registry maintains all the records for the domains that are responsible for. It records personal details of the registrant (the owner) but also very important technical details. This information is related to what nameservers a domain uses. To be more clear, a registrant can choose those nameservers that they are crucial for all the domain name system.
For example, if a registrant has a site they need to host is somewhere. Nameservers tell the whole world where this website is stored and they look like ns1.xycz.com, ns2.xyz.com.Registries can play the role of registrar (a retailer) too but usually, that is not the case.
Domain Name Resellers
Domain Name resellers are not accredited by ICANN and they have contracts with registrars. They usually offer other services too (such as hosting) and the actual responsible for domain registrations is the original registrar.
Domain Name Registries List
In this section, I am sharing a domain name registries list of the most popular domain name extensions.
Verisign is a US company that has a contract with ICANN to provide registry services for these domain names: .com, .net, .name, .cc, .tv, .edu, .gov and .jobs
Afilias is another company with headquarters in the USA and provides registry services for .info, .mobi, .pro, .pink, .blue, .black, .red, .kim, .shiksha, .organic, .dotchinesemobile, .lgbt, .vote, .voto, .green.poker, .promo, .bet, .pet, .bio, .ski, .archi, .llc
China Internet Network Information Center is responsible for .cn domain.
DENIC eG is a not-for-profit entity that manages the .de domain.
EURid is a non-profit that the European Commission assigned them the role of the registry for the .eu domain.
Nominet UK is another non-profit which is the registry for .uk domain.
AFNIC is the registry for .fr domain.
Coordination Center for TLD RU is the registry for .ru domain
I hope the post was helpful. If you would like to learn why do we pay for domain names with more details please check this post: Why Do Domain Names Cost Money (detailed explanation)